Cancer Biology and Oncology
Various types of cancers account for almost half of all disease related deaths in companion animals and are the second most common cause of death in people. With the exception of “childhood cancers” which typically reflect defects in developmental pathways, the incidence of cancer increases exponentially in the last third of the average lifespan of most species including human and represents the number one natural cause of death in older pets; in this and other respects cancer is therefore considered a disease of aging.
Studies into the causes of cancer have focused on the inherited and somatic mutations that activate oncogenic pathways and inhibit tumor suppressor pathways intrinsic to the transformed cancer cells and this remains a fruitful area of research on the basic mechanisms underlying the development of cancer and progression to metastatic disease which is the major cause of cancer related deaths and continues to provide targets for the development of novel therapeutics. However, it is now well-established that extrinsic signals provided by non-transformed cells and extracellular matrix are also critical to tumor initiation, progression and metastasis. Importantly, tumor stroma can confer resistance of many tumors against various therapeutic agents.
Our increasing understanding of these extrinsic mechanisms is revealing myriad of novel potential targets to inhibit tumor growth and to enhance delivery and efficacy of conventional tumor cell targeted therapies. Better understanding of causes and mechanisms of cancer development and progression is required for improving the prevention, diagnostics and treatment of veterinary and human cancer patients suffering from oncologic diseases. Members of the department are using cutting-edge technologies to conduct interdisciplinary studies in many areas of cancer biology including:
- Intrinsic oncogene and tumor suppressor pathways
- The tumor microenvironment
- The relationship between inflammation/fibrosis and cancer
- Mechanisms of age-tumorigenesis
- Cancer stem cells and cancer stem cell niche
- Drivers of metastasis and the metastatic niche
- Developing novel tumor and stromal cell targeted therapies including immune-based therapeutic modalities and small molecule therapeutics
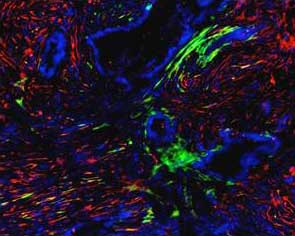
Human PDA
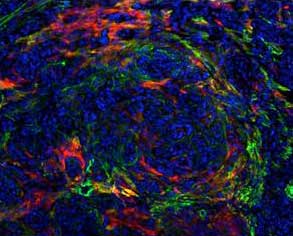
Murine PDA (KPC)
FAP/SMA/DAPI
Faculty
Contact the Biomedical Sciences Department
Our department is supported by a core of dedicated professional and administrative staff.
Department of Biomedical Sciences
216E Old Vet Quad
3800 Spruce Street
Philadelphia, PA 19104







