Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging
What we do
Our highly trained technologists and dedicated radiologists work together seamlessly to provide rapid and accurate diagnostic insights, ensuring your beloved pets receive the best care possible. Our range of imaging techniques, such as radiography, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine, help to effectively identify diseases and conditions in your pet.
Diagnostic Imaging Facilities
The radiology section is equipped with modern equipment, including two ultrasound machines, a 64-slice CT scanner, a 1.5T MRI scanner, and two digital radiographic suites, including fluoroscopy
Our Services
Process and Types of Imaging
Our services uses various imaging techniques, including radiography, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine, to identify diseases and conditions in animals.
Our Process
These imaging services are performed by trained staff, with the exception of ultrasounds, which are conducted by radiologists. A report is generated within hours after interpreting the images and the findings are shared with the primary veterinarian. Digital images can be sent to the referring veterinarian and stored on a remote server for future access.
To keep the animal still during imaging, sedation or general anesthesia is often required, with supervision provided by experienced anesthesia professionals. For ultrasounds, the animal’s hair may need to be clipped to ensure clear imaging. Radiographic dyes are sometimes used to enhance visibility during CT, MRI, and certain radiographic procedures. These dyes are selected for their safety, and the animal is closely monitored throughout the process. The machines employed for human imaging are adapted for veterinary use, with adjusted doses and protocols, ensuring accurate and safe diagnostic imaging through a highly trained veterinary radiology team.
Digital Radiography
Description of Service and Procedures
Digital radiography is use to evaluate the thorax (chest),, abdomen, spine and extremities (legs). Digital radiography is also use for advanced contrast procedures such as pyelogram, cystograms, gastrointestinal contrast studies and more.
Estimated Time for Completion of Service
Typical time to completion is less than one hour, depending on caseload.
Procedures
All radiographs are obtained by highly trained and skilled veterinary radiology technologists. They ensure that the procedure is performed as smoothly and fast as possible, while guaranteeing excellent image quality, thereby allowing maximal diagnostic accuracy.
Images are reviewed within minutes by board-certified radiologists.
Contrast studies are performed under the supervision of the attending radiologist.
Fluoroscopy
When an animal experiences difficulty breathing or swallowing, a veterinarian may recommend fluoroscopy as a diagnostic tool Fluoroscopy is used when we try to see inside of the body while the organs are in motion. For example, fluoroscopy is used to view tracheal collaps, heart or lung issues, and problems an animal may be experiencing while it tries to swallow.
Fluoroscopy is used to diagnose problems such as:
- Blood flow through vessels that are abnormal
- Tracheal collapse
- Problems within the gastrointestinal system
- Difficulty swallowing involving abnormal strictures
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound imaging options include:
- Abdominal
- Non-Cardiac
- Thoracic
- Cervical ( Thyroid, Parathyroid, Salivary glands and lymph nodes)
- Musculoskeletal
- Ocular
Additional services include:
- Ultrasound-guided aspiration
- Biopsy procedures
Description of Service and Procedures
The ultrasound imaging service provides abdominal, non-cardiac thoracic, musculoskeletal and ocular ultrasound, US-guided aspiration, and biopsy procedures. If clinically indicated, we can also perform contrast-enhanced ultrasound, which is useful in characterizing benign from cancerous lesions, primarily used in liver imaging.
Procedures
- All our ultrasound examinations are performed and/or finalized by a radiologist. None of the studies are performed by a technologist.
- Abdominal hair will need to be clipped to allow for adequate ultrasound evaluation oRyan Patient Mango undergoing ultrasoundf the patient.
- Patient fasting is needed for ultrasound examinations. Please be aware that patients should be fasted at least eight hours before the examination to prevent food and gas interference. Pediatric or Diabetic patients should call the radiology department for feeding recommendations.
- The examination itself lasts approximately 30 minutes after which a report is quickly generated and made available to the primary clinician.
- Occasionally, sedation or anesthesia will be needed if the animal is stress or painful. Sedation or anesthesia will always be needed for ultrasound guided biopsies and aspirates.
- The duration of anesthesia is generally short, and the patient is monitored using sophisticated equipment including electrocardiogram, blood pressure and respiratory devices. Modern anesthesia drugs allow for quick onset of and recovery from anesthesia. Under direct supervision by a board-certified anesthesiologist, anesthesia is administered by highly trained veterinary nurse-anesthetists who select the drugs and administration protocol according to each patient’s individual requirements.
High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
What Is MRI?
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses magnetic fields to look inside of humans and animals.
- Highly detailed images are generated from magnetic signals, which experienced veterinary radiologists then view and interpret via computer, allowing our clinicians to more accurately determine causes and locations of animal diseases and abnormalities.
Why Use MRI Technology?
Many diseases and conditions can be better diagnosed using MRI technology.
- Neurologic diseases or cancer
- Brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
- Imaging of the spine for tumors, infection, trauma or intervertebraldisc disease or herniation
- Musculoskeletal abnormalities including, tendon, ligament or muscular tear, tumor or infection
- Hepatic neoplasm and metastatic disease
- Renal, adrenal, pancreatic neoplasm
- Portosystemic shunt or other congenital or acquired vascular abnormalities evaluation
- Vascular thrombus or tumor
- Surgical planing
What to Expect
Veterinary patients must be anesthetized to undergo a MRI scan, since they must remain absolutely still during the procedure.
- The duration of anesthesia depends on the study needed, but usually last 1.5 to 2 hours.
- The patient is monitored using sophisticated equipment including electrocardiogram, blood pressure and respiratory monitoring devices.
- Modern anesthesia drugs allow for quick onset of and recovery from anesthesia.
- Under direct supervision by a board-certified anesthesiologist, anesthesia is administered by highly trained veterinary nurse-anesthetists who select the drugs and administration protocol according to each patient’s individual requirements.
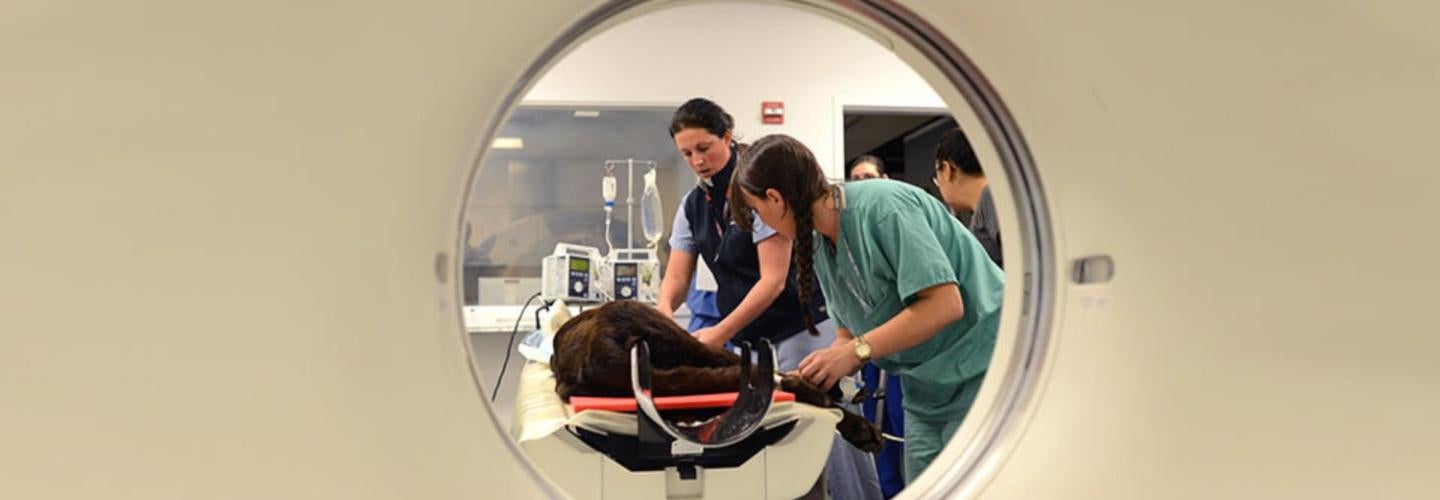
Computed Tomography (CT)
The computed tomography service currently provides CT examinations of head, thorax (chest), abdomen, spine, musculoskeletal systems, and CT vascular studies.
A multislice CT unit was installed in 2009 and is housed in the Rosenthal Imaging and Treatment Center (RITC). This CT scanner allows for rapid acquisition of cross-sectional images. This significantly decreases the time to complete a scan and therefore duration of anesthesia and also provides images with superb resolution. In conjunction with the latest computer software multi-slice CT permits evaluation of blood flow within the body and dynamic assessment tumor perfusion.
Procedure
Veterinary patients must be anesthetized for CT, since they must remain absolutely still during Penn Vet, Ryan Hospital, radiology, catscanthe treatment. The duration of anesthesia is generally short, and the patient is monitored using sophisticated equipment including electrocardiogram, blood pressure and respiratory monitoring devices.
Modern anesthesia drugs allow for quick onset of and recovery from anesthesia. Under direct supervision by a board-certified anesthesiologist, anesthesia is administered by highly trained veterinary nurse-anesthetists who select the drugs and administration protocol according to each patient’s individual requirements. Most cases require injection of iodinated contrast agents.
Our Care Team

Chief, Section of Radiology
Wilfried Mai, DMV, PhD, MSc, DECVDI, DACVR
Professor of Radiology
Veterinarians

Yael Porat-Mosenco, DVM, DECVDI, DACVR

Jennifer Reetz, DVM, DACVIM, DACVR

Robert Slater, BVMS (Hons), MRCVS, DACVR
Residents

Julia Fox, DVM

Natalie Goolik, DVM, DACVR

Maryam Iranmanesh, DVM

Robb Kessel, VMD

Rocio Remolina-Palomino, DVM, MsC

Yu (May) Wang, DVM

Robert Wise, DVM, DACVR

Jin Yu, DVM
Cheryl A. Diehl
Manager, Imaging Services
Russell White, RT (R) (MR)
MRI Technologist
Barbara Kaminsky, RT
Chief Technologist
Elizabeth Baldwin, CVT
Radiology Veterinary Nurse
Amy Dilling CVT, RT, (R), (CT)
Radiology Veterinary Nurse
Aaron Flannery, CVT Eligible
Radiology Veterinary Nurse
Jennifer Marone, CVT
Assistant Supervisor
Radiology Veterinary Nurse
Ryan Veterinary Hospital
Emergencies:
(215) 746-8911
By Appointment:
(215) 746-8387



