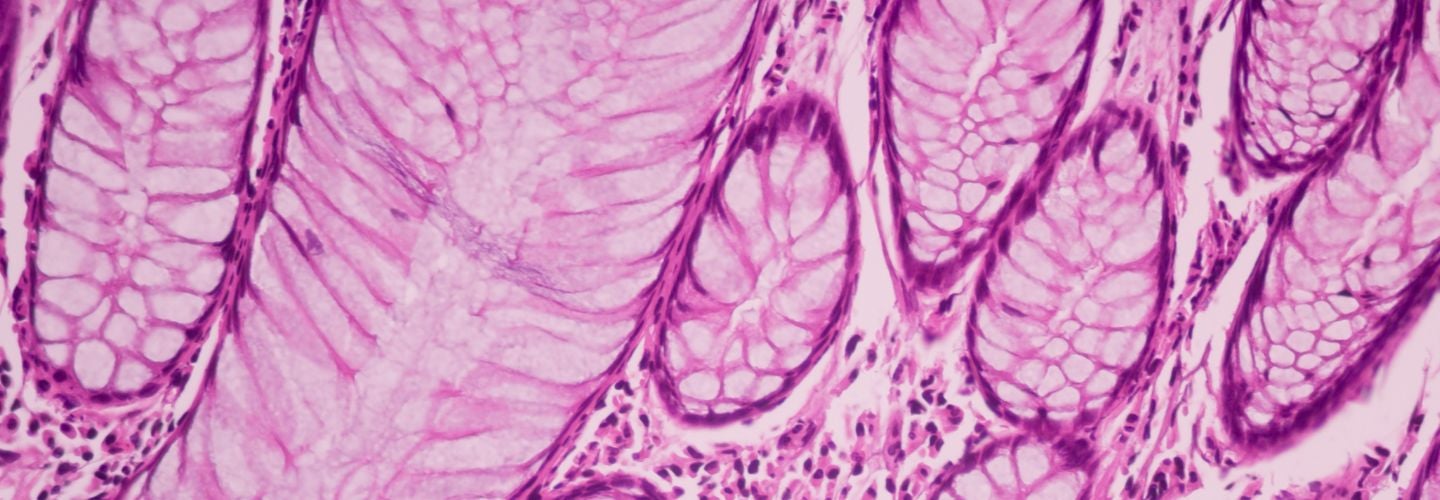
Penn Vet Cancer Center
what we do
The Penn Vet Cancer Center is where cutting-edge research meets compassionate care. It’s where human and veterinary medicine converge. It’s where Penn Vet leads the field.
In the Lab
Scientists are conducting the essential basic research that grounds cancer breakthroughs. Collaborators from the School of Veterinary Medicine, School of Medicine, and partnering institutions are working together to share and build knowledge in new and collaborative ways. By breaking boundaries between animal and human medicine — between disciplines and practice — critical links can be made in advancing global cancer research.
In the Clinic
Veterinarians are applying scientific discoveries that lead to patient success stories. With an integrated approach to cancer care, including clinical trials and novel therapies, clinicians are diagnosing and treating pets at the vanguard of veterinary medicine. At the core of their work is expertise and empathy, and at the center of their impact is pets and their owners.
In Collaboration
The Penn Vet Cancer Center bridges the laboratory and the clinic for a collaborative approach to cancer’s biggest questions. The result is new dialogue and integrated frameworks that move toward one shared goal: the prevention and treatment of cancer in all species.

Cancer Research
Research at the Penn Vet Cancer Center supports our mission to:
- Sponsor training in Cancer Biology and Clinical Oncology.
- Explore the causes of cancer to inform cancer prevention.
- Develop new diagnostics, prognostics, and therapies for veterinary and human cancer patients.
- Provide interdisciplinary clinical care of veterinary oncology patients.
Vet School Partnerships
The Penn Vet Cancer Center works closely with clinicians at Ryan Hospital and administrators of clinical trials.

Comprehensive Cancer Care
Learn how the Cancer Center partners with Ryan Hospital to approach to cancer care.

Clinical Trials
Find out about how the Cancer Center participates in research trials.
Center Highlights
- M. Andrés Blanco, an assistant professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine, and his colleagues have identified a new approach to triggering differentiation in AML—one with potential to treat a much wider array of AML patients. Their study, published in the journal Cancer Discovery, identifies an enzyme that regulates the process by which AML cells differentiate. In both cell lines and an animal model, the researchers found that inhibiting this enzyme, particularly in combination with other anti-cancer therapies, prompted AML cells to lose aspects of their identity associated with aggressive growth. The cells also began to exit the cell cycle, on the path toward maturing into a new cell type.
- For dogs with osteosarcoma (a cancer of the bone) the standard treatment has been amputation combined with chemotherapy, and even that rarely staves off the cancer’s spread. Nicola Mason is embarking on a new way to treat the disease, using a novel immunotherapy-based vaccine to prevent metastasis to other organs.

Our Members
The Penn Vet Cancer Center is comprised of research scientists and clinicians from all four departments of the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine.
Support Our Work
Learn about our funding and how to make a donation to support our ongoing innovative cancer research.
Find Us
University of Pennsylvania
School of Veterinary Medicine
3800 Spruce Street
Philadelphia, PA 19104-4539
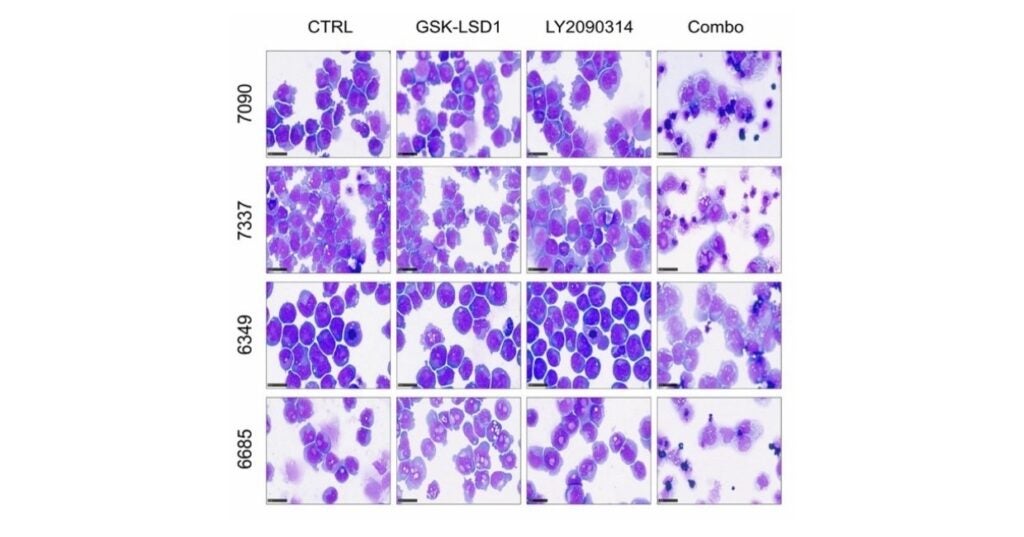
New Study Identifies Promising Inhibitor Combination for Hard-to-Treat Leukemia Subtypes
Faculty In This Story Assistant Professor of Biomedical Sciences M. Andrés Blanco, PhD, from the University of Pennsylvania’s School of Veterinary Medicine (Penn Vet) and investigators from the Universities of…
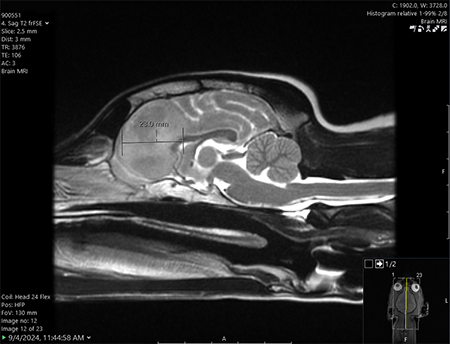
One Tiny Dog’s Outsized Contribution to Brain Surgery
Geddy Lee has lived a big life for a little dog. As a puppy, the tiny terrier mix was abandoned in Mississippi during a high-speed car chase. Rescued by law…

Study shows promise for iNKT cell platform to treat cancer (link is external)
Researchers from the School of Veterinary Medicine and Perelman School of Medicine have shown that invariant natural killer T cells from a healthy donor can persist in MHC-mismatched canines, demonstrating…
Penn Vet Cancer Center
Email: cancercenter@vet.upenn.edu
3800 Spruce Street
Philadelphia, PA 19104
